Technology has changed the way business and customers interact with one another. Interactions between a business and customer occurs during the information search process a customer undertakes. The internet acts as both a distribution and communication channel (Rose et al. 2011, p. 24). The growth of e-commerce in Australia is increasing. As of 2017, 85% of Australians are engaging with the internet and an estimated 12.1 million are on social media platforms (TransDirect 2018). Online transactions are more convenient for customers these days with customers using online businesses to purchase goods and services (TransDirect 2018).
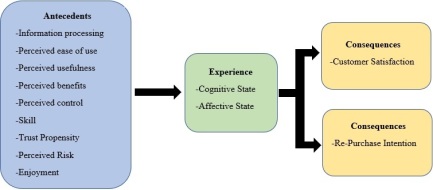
This post will discuss my online customer experience of using Platypus’s website. I will be using Rose and Hair’s (2011) online customer experience framework to discuss my personal experience. Rose and Hair’s framework consists of 8 components: information processing, perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived benefits, perceived control, trust and risk, and enjoyment. The components can positively or negatively influence or motivate the customer’s experience (Chaffey & Ellis-Chadwick 2016, pp. 77-78).
Information Processing
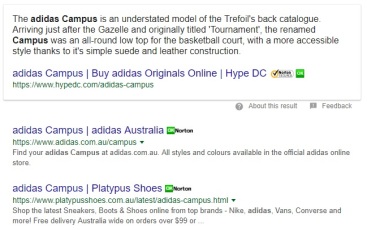
Information processing is how a consumer analysis all the available information that will influence their purchase behavior (Chaffey & Ellis-Chadwick 2016, p. 77). During my purchase process I had a specific product in mind which made me a directed buyer. I typed Adidas Campus into Google and Platypus was the 3rd search result. As I have previously had a positive purchase experience and prior knowledge at Platypus I decided to use their website.
Perceived Ease of Use and Perceived Usefulness
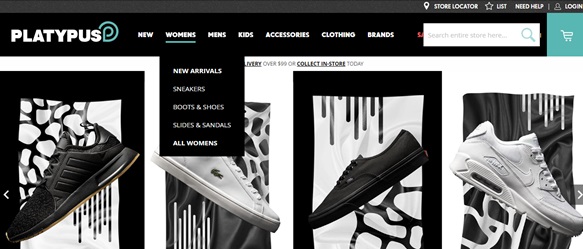
When a consumer visits a website the ease of using that site will influence their online experience (Chaffey & Ellis-Chadwick 2016, p. 77). The site’s layout and design should be easy to use as this will influence the consumers online experience (Digital Communications 2016). Platypus’s site is easy to use and the layout of the site made it easy for me to find what I needed easily. Customers can navigate the site through different categories, allowing for ease of use.
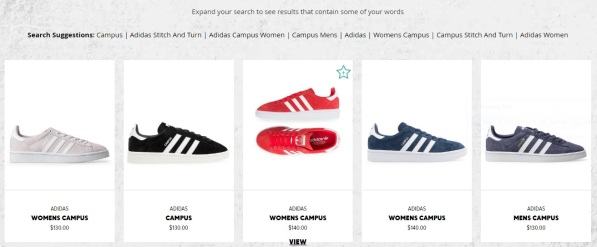
Perceived usefulness is how useful the site to customers. For example, does the site have a search facility, and the responsiveness of the site. How accurate and relevant is the information of the site (Digital Communication 2016). My experience with Platypus’s site is positive as I found my product quickly; the search option took me directly to my product.
Perceived Control & Skill
Customers that are skilled with technology will feel they are in control when using websites. The importance of customers feeling confidence when using websites must be understood by organisations as these experiences influences future purchase behavior (Chaffey & Ellis-Chadwick 2016; Digital Communication 2016). The skills I possess ensures I am in control of what I view and how I navigate Platypus’s website.
Perceived Benefits
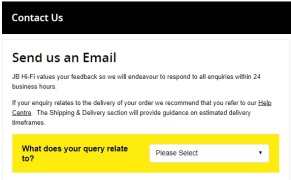
Consumer are getting more familiar and comfortable with using online businesses as the technology adoption and infrastructure are improving day by day (Nielsen 2016, p. 4). Nielsen (2016, p. 22) state that there are a variety of reasons customer prefer to shop online. The convenience of shopping online reduces time and effort compared to being in a physical store. Access to a wider range of products and better deals. I personally do not shop online usually but as I did not have time to go to the physical store I decided to shop online. Platypus promotes that they do same day delivery as seen in the picture below. The second picture demonstrates how Platypus’s customers can sign up for their newsletter which informs customers with sales, competitions, products and the chance to win vouchers.
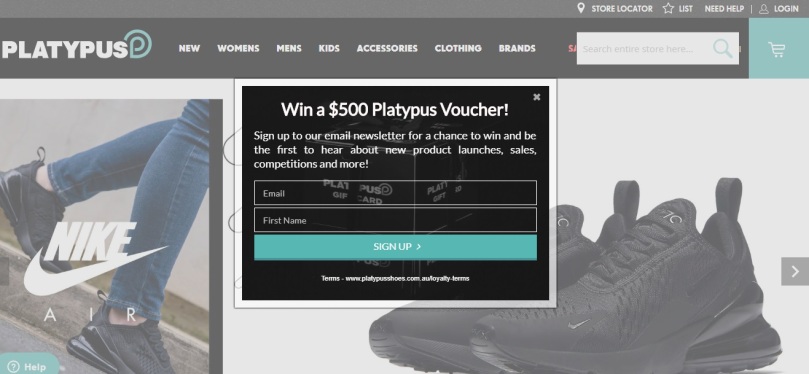
The website is easy to navigate and quickly allowed me to find my shoes. My overall online customer experience with Platypus was positive. In the future I will continue to use their websites to make purchases.
Quick question for everyone… How do you find your online customer experience when making purchases, and do they differ depending on the product or service?
Reference
Chaffey, D & Ellis-Chadwick (eds) 2016, Digital Marketing, Pearson, UK
Digital Communications 2016, ‘The online customer experience’, Digital Communications, web log post, viewed 30th August 2018, <http://www.digitalcommunications.net.au/2016/08/28/the-online-consumer-experience/>
Nielsen 2016, Global connected commerce, is e-tail therapy the new retail therapy, Nielsen, viewed 30th August 2016, <http://www.nielsen.com/content/dam/nielsenglobal/jp/docs/report/2016/Nielsen-Global-Connected-Commerce-Report-January-2016>
Rose, S, Hair, N & Clark M 2011, ‘Online customer experience: a review of the business to consumer online purchase content’, International Journal of Management, vol. 13, pp. 24-39.
TransDirect 2018, ‘The exploding growth of ecommerce in Australian: 4 statisitics you need to know’, TransDirect, web log post, viewed 28th August 2018, <https://www.transdirect.com.au/blog/aus-ecommerce-stats>